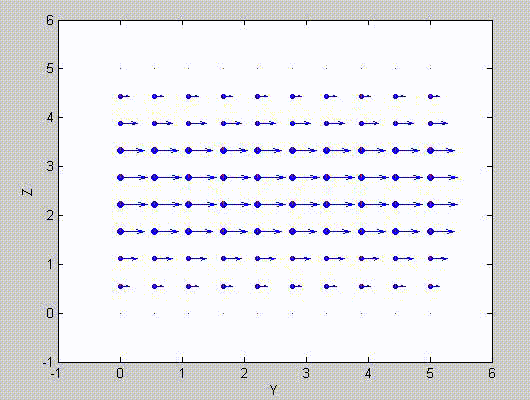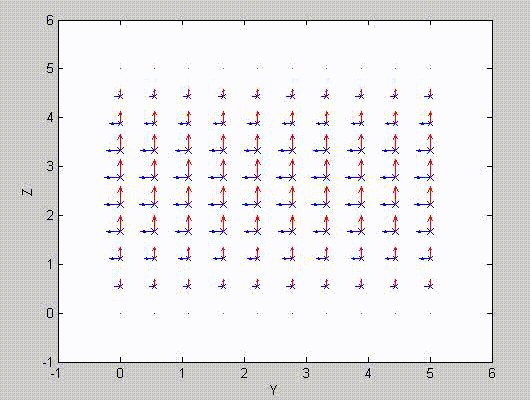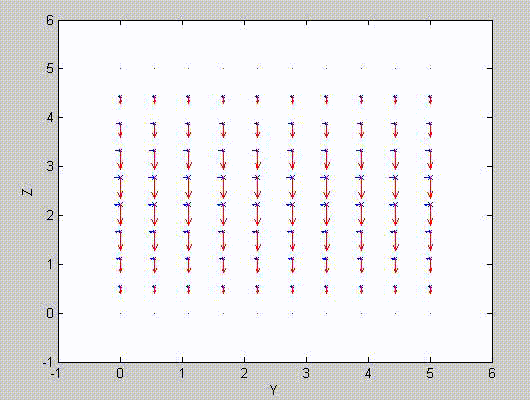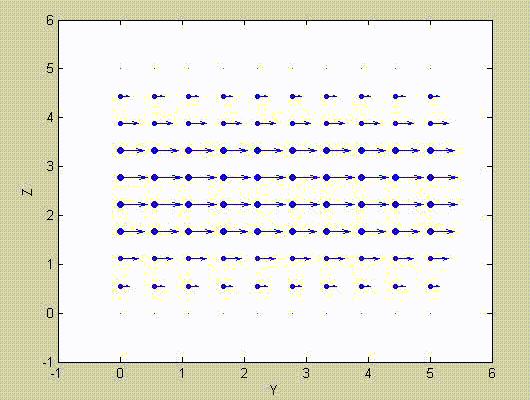
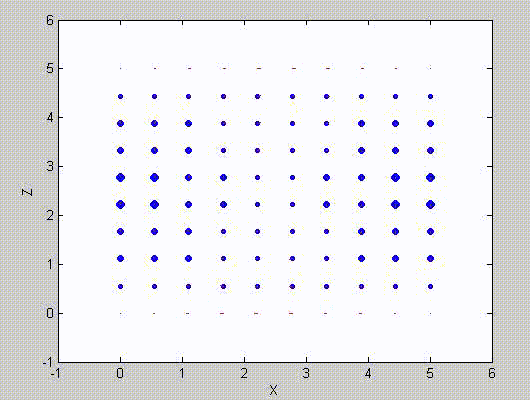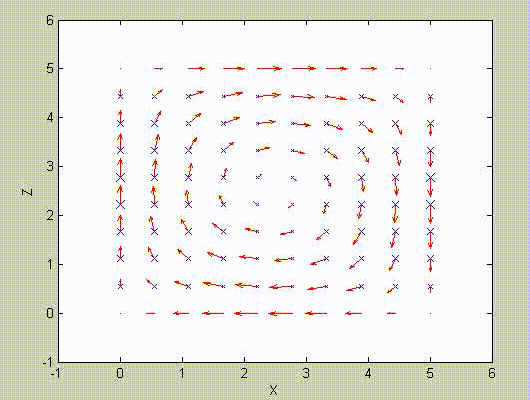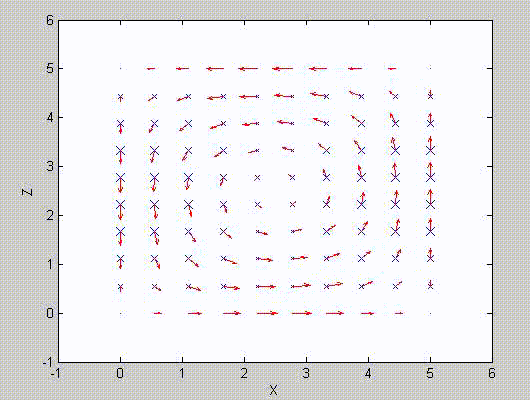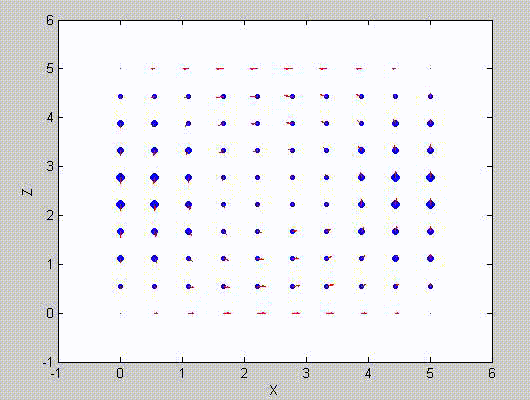
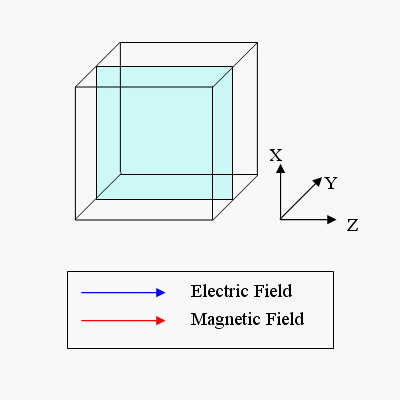
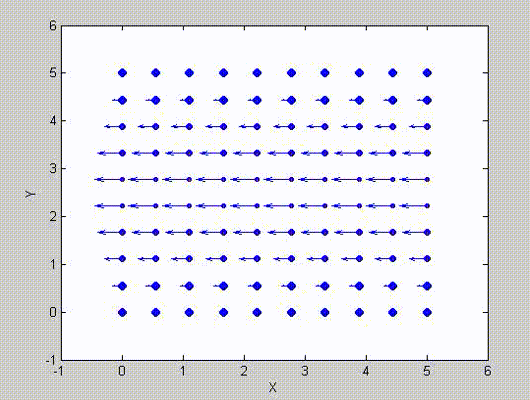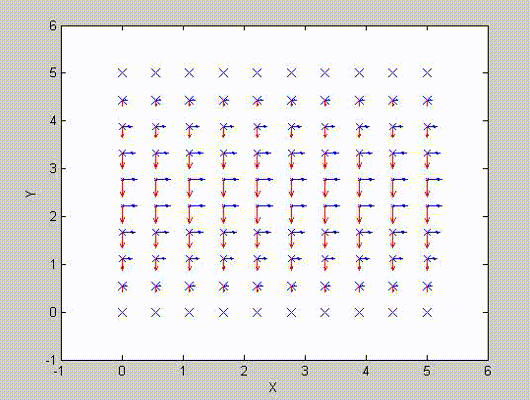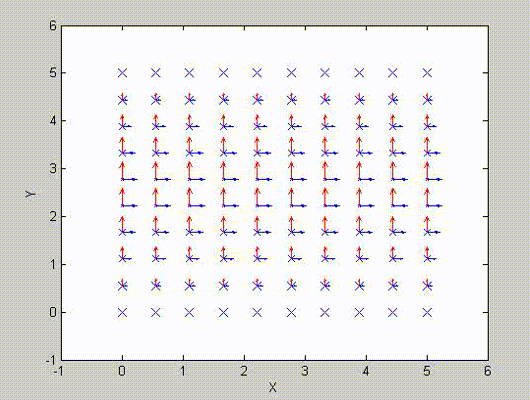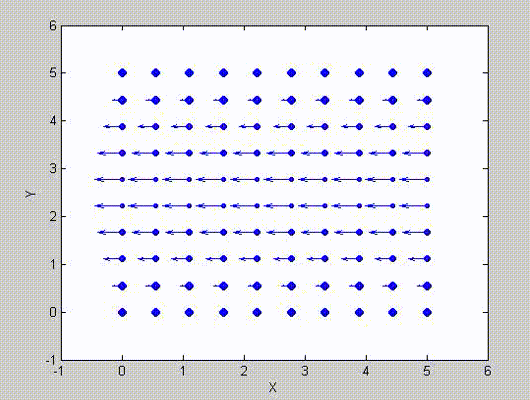
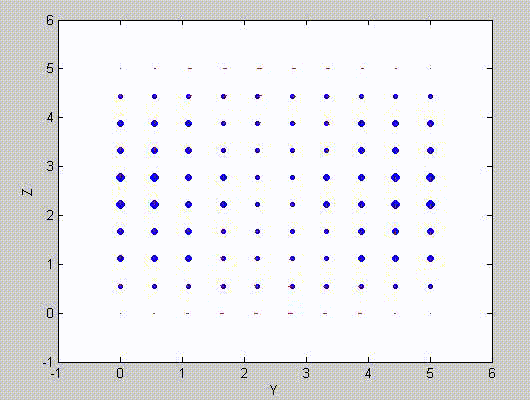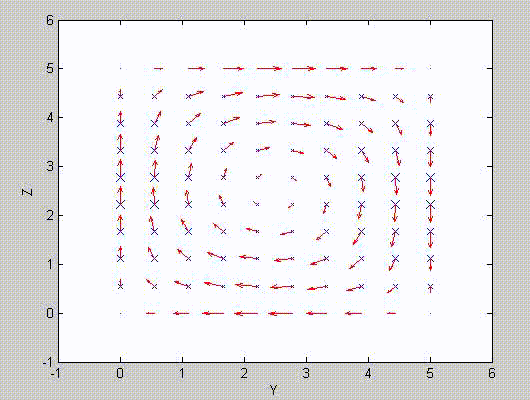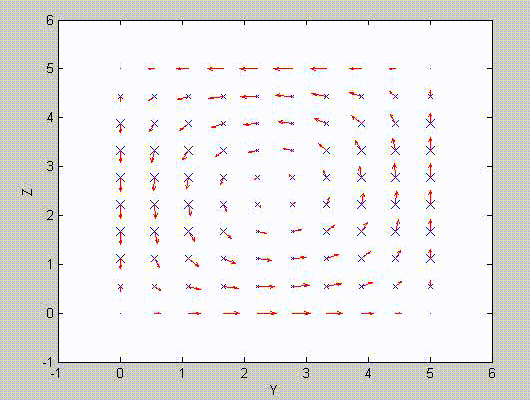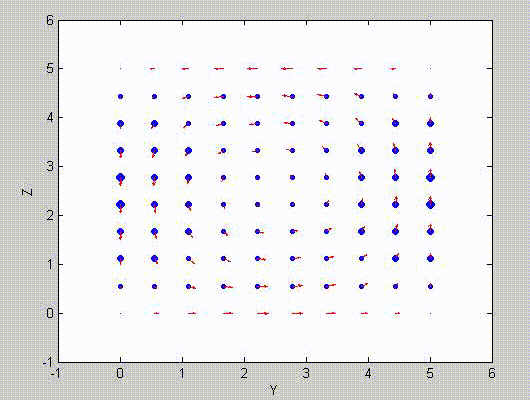
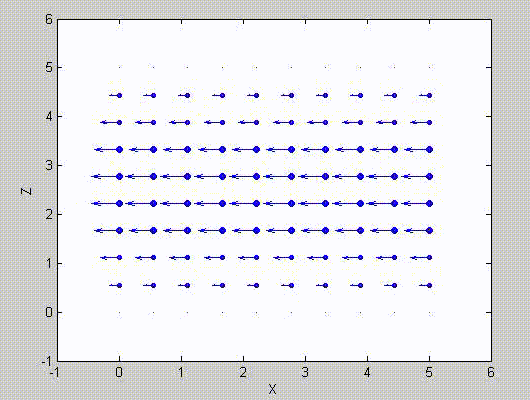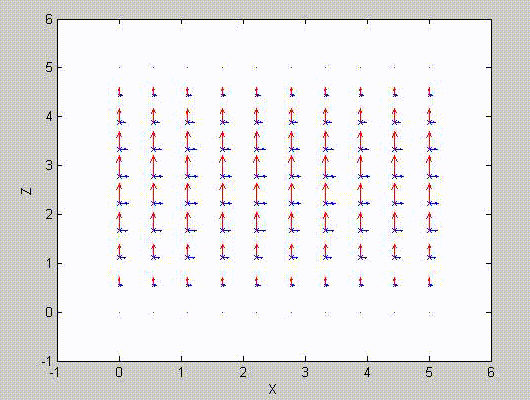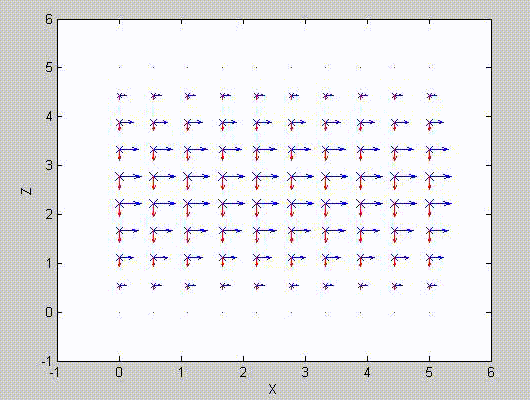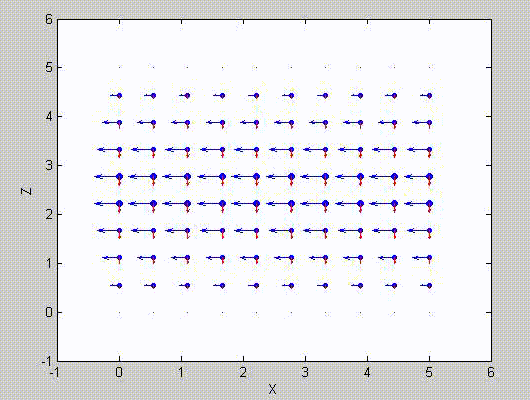
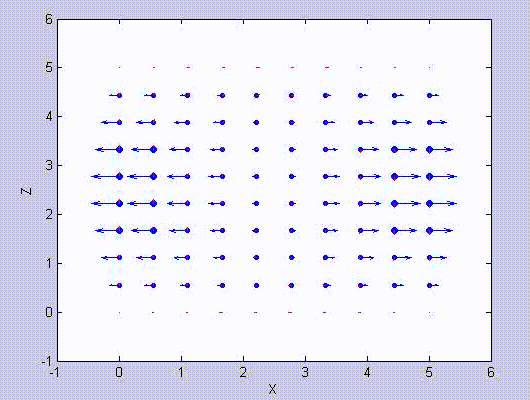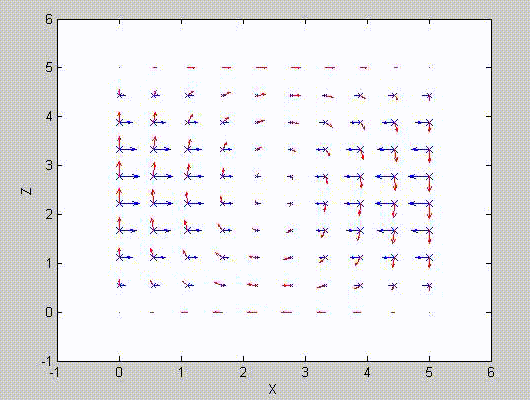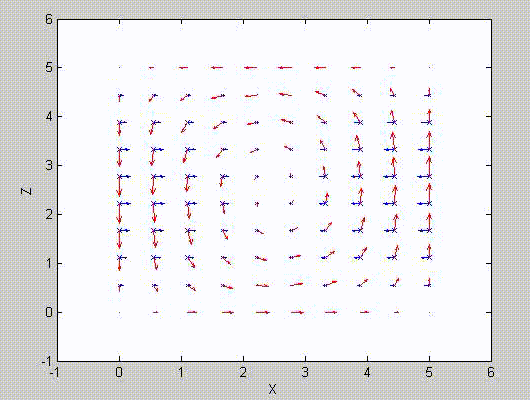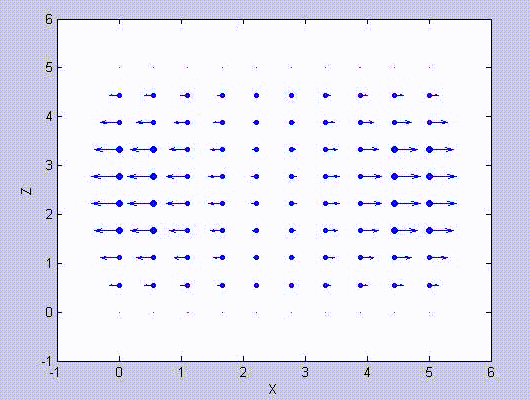
There are two sets of modes, TE modes and TM modes, that can exist in a rectangular cavity resonator as shown in Fig.1.13.
Following the same procedure as in the last section, the transverse electric and magnetic fields can be expressed in terms of the Ez and Hz components which satisfy the wave equation. The boundary conditions require that (1) Ey = Ez = 0 at x = 0 and x = a, (2) Ez = Ex = 0 at y = 0 and y = b, and (3) Ex = Ey = 0 at z = 0 and z = d.
As a result, standing-wave forms are taken in all the x̂, ŷ, and ẑ directions, and three sets of guidance conditions are obtained as kx = mπ/a, ky = nπ/b, and kz = pπ/d.
For the TE mode, Ez = 0, and
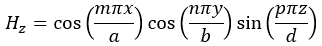

with m, n = 0, 1, 2, ···, m2 + n2 ≠ 0, p = 1, 2, ···. The wave numbers and the frequency satisfy the dispersion relation (mπ/a)2 + (nπ/b)2 + (pπ/d)2 = ω2με. Thus, the resonant frequency of the TEmnp mode can be expressed as
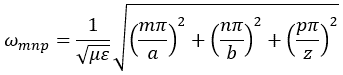
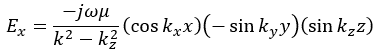
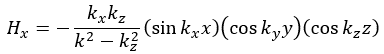
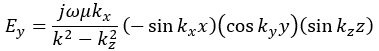
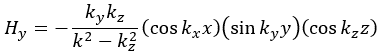
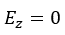
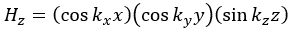
a = 5, b = 5, d = 5