N-Element Linear Array
Editor: 劉志祥 、李宜音 、陳純熙
Adviser: 江簡富教授
Fig.1.7(a) shows an array of N
identical electric dipoles lying along the z axis. The separation
between two adjacent dipoles is d, and the phase of the feeding currents
is incremented by ![]() progressively
from dipole to dipole. The array factor of this array can thus be expressed as
progressively
from dipole to dipole. The array factor of this array can thus be expressed as
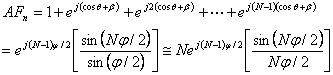
where
![]() .
The last approximation is valid when
.
The last approximation is valid when
![]() is
small.
is
small.
The item in the bracket is the normalized array factor with maximum amplitude of unity.
Nulls of the array factor can be
derived by setting its numerator to zero while keeping it denominator
nonvanishing. Thus, we have ![]() but
but
![]() ,
where n and p are arbitrary integers. The associated directions at
nulls are
,
where n and p are arbitrary integers. The associated directions at
nulls are![]() .
Maxima of the array factor occur when
.
Maxima of the array factor occur when
![]() with
m an arbitrary integer, and the associated directions are
with
m an arbitrary integer, and the associated directions are![]() .
The direction with radiation intensity half that of the maximum can be found by
setting
.
The direction with radiation intensity half that of the maximum can be found by
setting ![]() .
Thus, we have
.
Thus, we have ![]() or
or![]() .
The half-power beamwidth can then be obtained as
.
The half-power beamwidth can then be obtained as
![]() ,
where
,
where ![]() is
the maximum direction with m = 0.
is
the maximum direction with m = 0.


Directions of
the side lobes can be approximated by setting![]() ,
and the associated directions are
,
and the associated directions are ![]() with
s
= 1,
2,
3,
· ·
·. The
first side lobe appears at
s
= 1, and the
associated magnitude of normalized array factor is
with
s
= 1,
2,
3,
· ·
·. The
first side lobe appears at
s
= 1, and the
associated magnitude of normalized array factor is
![]() or
13.46
dB lower than the maximum amplitude.
or
13.46
dB lower than the maximum amplitude.
Figs.1.7(b)
and (c) show the array factor with different element separations. When
![]() ,
the maximum occurs at
,
the maximum occurs at![]() ,
perpendicular to the array axis. Thus, the array is called the broadside array.
When the element separation is increased to
,
perpendicular to the array axis. Thus, the array is called the broadside array.
When the element separation is increased to![]() ,
other maxima also appear in the axial direction, also called the end-fire
direction. The maxima other than the major lobe are called grating lobes. The
grating lobes can be avoided by restricting the element separation to less than
one wavelength.
,
other maxima also appear in the axial direction, also called the end-fire
direction. The maxima other than the major lobe are called grating lobes. The
grating lobes can be avoided by restricting the element separation to less than
one wavelength.
The major lobe
of an array can be steered toward different directions by changing the
progressive phase,![]() .
Such an array is called phased array or scanning array. The half-power beamwidth
of an array decreases when the number of array elements increases. However, the
half-power beamwidth of the major lobe usually increases when it is steered
toward the end-fire directions.
.
Such an array is called phased array or scanning array. The half-power beamwidth
of an array decreases when the number of array elements increases. However, the
half-power beamwidth of the major lobe usually increases when it is steered
toward the end-fire directions.
![]()
Distribution of Power Density
Distribution of Field and Power Density
![]()
Distribution of Power Density
![]()
Distribution of Field and Power Density
![]()
![]()