Single Stub Matching
Editor:張宏彬
Advisor:江簡富

(I) Analytic Approach
![]()
![]()

where n is
an integer (positive or negative). The amplitude and
phase of ![]() are
are
![]()
![]()
The parameter ![]() and
and ![]() can be expressed in terms of
can be expressed in terms of ![]() and
and ![]() as
as
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
Two possible solutions for b and ds
are given in (1) and (2) respectively, where the integer value for n
is chosen such that ![]() .
.
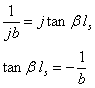

(II) Smith Chart Approach
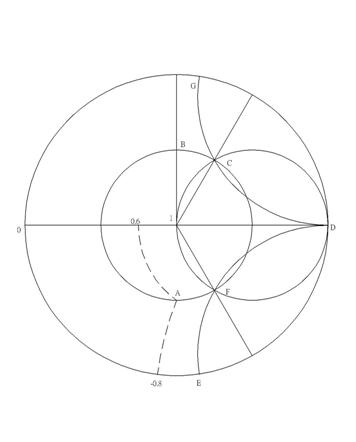
(a) ![]() => point A
=> point A
(b) Drawing constant SWR circle passing through A, go around the
constant SWR circle by half a revolution to B which corresponds to ![]()
(c) The constant SWR is also the locus of ![]()
![]() . Draw r = 1 circle and find C
and F which correspond to two solutions of
. Draw r = 1 circle and find C
and F which correspond to two solutions of ![]() . The distance moved from B to C is the
location of stub.
. The distance moved from B to C is the
location of stub.
![]()
(d) Since the short circuit corresponds to a susceptance of infinity, we start at point D
(the outmost
circle) to reach E which is the input admittance of the stub normalized with![]() . The distance moved
from D to E is the length of the stub.
. The distance moved
from D to E is the length of the stub.
![]()
(e) The second solution of ![]() can be obtained from
(c), which is the distance moved
can be obtained from
(c), which is the distance moved
from B to F.
![]()
(f) The second solution of ![]() can be obtained from (d).where
can be obtained from (d).where ![]() is the distance from
D to G.
is the distance from
D to G.
![]()
Parameter in DEMO:
![]() ,
,![]()
=>![]()
The general expressions for the line voltage and line current are
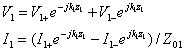
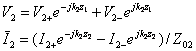
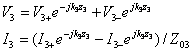
the waves satisfy the boundary condition given by:
(1) at ![]() =0
,
=0
, ![]()
(2) at ![]() =0
,
=0
, ![]()
(3) at ![]() =0
,
=0
, ![]()
(4) (5) at ![]() =0,
=0,
![]() =
=![]() ,
,![]() =
=![]() ,
, ![]()
(6) ![]()
Form above , we can obtain voltage and current in which region as follows:
Region 1:
Region 2:
Region 3: