Polarization of Electric Field
Editors : ���T �B ������ �B �G���
Advisor : Professor Jean-Fu
Kiang
By definition , polarization is the
characteristic that describes how the direction of time varying field
oscillating at a point in space changes with time . Here we discuss about electric
field in EM-wave . To simplify the discussion , we decompose the electric field
into two direction , ![]() and
and ![]() , as two components
, and let it propagate in the
, as two components
, and let it propagate in the ![]() direction . For a
uniform plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction , that is :
direction . For a
uniform plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction , that is :
![]() , where
, where ![]() is the direction of propagation
, or the wave number vector ,
is the direction of propagation
, or the wave number vector ,
where ![]() is the position vector , such as
is the position vector , such as ![]() in Cartesian coordinate .
in Cartesian coordinate .
We
consider that if the wave propagating in ![]() direction , then
direction , then
![]() with
with ![]() =
=![]()
Here
we use the phasor notation![]() and
and![]() be two decomposition in the
be two decomposition in the ![]() and
and ![]() direction .
direction .
Then
the total electric field can be represented :
![]()
Let![]() and
and![]() have
a phase difference of �p ,
and amplitude ratio of
have
a phase difference of �p ,
and amplitude ratio of ![]() direction to the
direction to the ![]() direction is A , namely
, and
direction is A , namely
, and ![]() ,
,
thus ,
we have : ![]()
Analyze the
polarization at a fixed point , that is , fixed z=0 .We will demonstrate
several situation in A (amplitude) and�p(phase angle) . Note that ![]() and amplitude of
and amplitude of ![]() is
is ![]() , and
we demonstrate the electric field��s
oscillating direction and amplitude as a vector.
, and
we demonstrate the electric field��s
oscillating direction and amplitude as a vector.
Case (1) : �p=0 ( Linear Polarization )
![]()
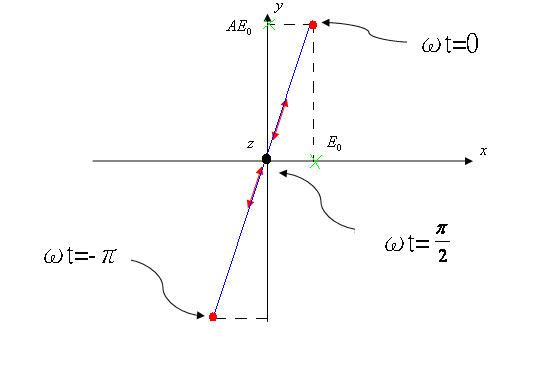
Since the electric
field oscillates along a line , it is called linear polarization .
Case (2)
: �p=![]() , A =1 ( Circular Polarization )
, A =1 ( Circular Polarization )
![]()
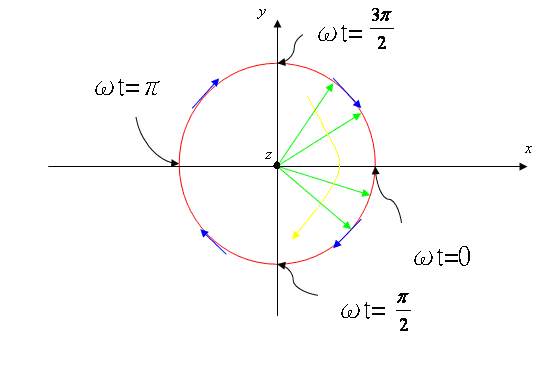
The electric field��s
oscillating direction and amplitude vector will rotate on a circle , hence it
is called circular polarization .
Case (3)
: A��1 , �p=![]() ( Elliptical
Polarization )
( Elliptical
Polarization )
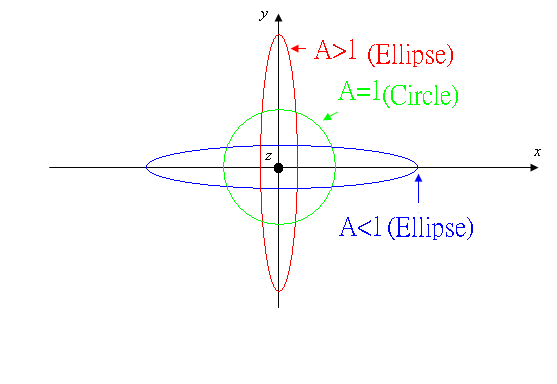
The electric field��s
oscillating direction and amplitude vector will rotate on an ellipse , hence it
is called elliptical polarization .
l
Left-hand
and Right-hand Polarization ( LH. and RH. ) :
If the vector
rotates in the clockwise sense , we call it right-hand polarization , i.e. as t
increases , the phasor angel of electric field will decrease. On the other hand
, it will rotate in the counterclockwise sense and is called left-hand polarization
.
For example , case
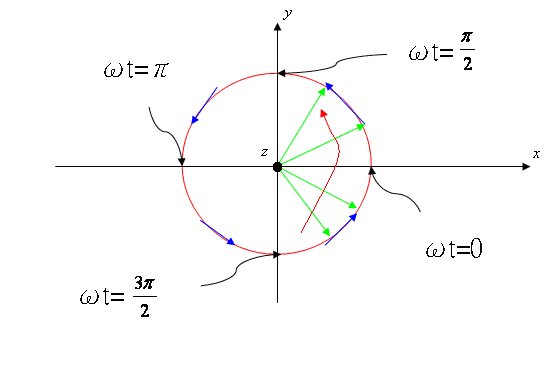
(2) is left-hand polarization . If �p=![]() , we have a right-hand
polarization :
, we have a right-hand
polarization : ![]()
(1) Linear polarization
Aerial view and x-y cross-sectional view
|
|
(2) Right-hand circular polarization ( RHCP )
Aerial view and x-y cross-sectional view
|
|
Perspective view on z - axis
|
|
(3) Left-hand
elliptical polarization ( LHEP ) : A = 0.5
|
Aerial view and x-y cross-sectional view
Perspective view on z- axis
|
(4) Left-hand
elliptical polarization ( LHEP ) : A = 2
Aerial view and x-y cross-sectional view
|
Perspective view on z- axis |